Review Thermaltake Power Express 650 – Affordable Power for Your High-end Graphics
Test Platform
We used the following hardware combination in our test.
- Processor : Intel Core i7 930 @4 GHz (200×20)
- Motherboard : Gigabyte X58A-UD3R
- Graphics card : 2xAMD Radeon HD 6870; NVIDIA GTX 480; 2xNvidia GTX 580
- Memory : 3×1GB Kingston KHX16000D3T1K3/3GX
- Harddisk : Western Digital Caviar Black 500 GB (32 MB Cache)
- Power Supply : Gigabyte Superb 460 Watt, Thermaltake Power Express 650W
- Heatsink : Gelid Tranquilo
- Monitor : Philips 221E
- Input Devices: Genius (Keyboard and Mouse)
- OS : Windows 7 Ultimate 32-bit
- Driver : Catalyst 10.10e; Forceware 260.99/262.99
- Casing: Venom RX Mid Tower
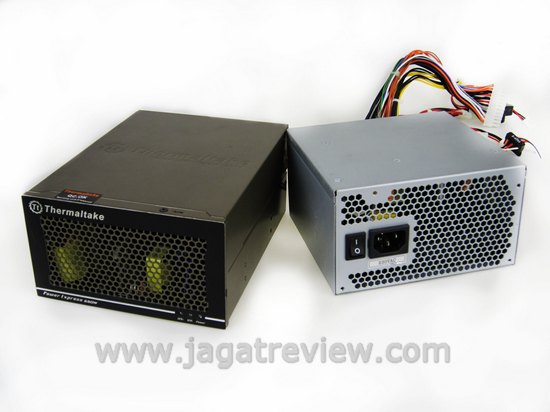

A 460-watt entry level PSU was used to power up the entire system, except the graphics cards of course, since we were using Thermaltake’s Power Express 650 to power those up. Our entry level PSU costs around US$ 40. Add the Power Express 650, and the two power supplies would only set us back around US$ 80-90. That’s relatively cheaper than buying a 1000 watt + PSU to get the same amount of output.
Test Results
The Power Express 650 was tested using several different graphics cards, starting from the Radeon HD 6870, GeForce GTX 480, to NVIDIA’s latest current cream of the crop, the GeForce GTX 580. Multi-graphics configurations (SLI and Crossfire) were also thrown into the fray.
Sythetic benchmarks, the 3D Mark Vantage and Unigine, were used to simulate power consumption in every day usage. Graphics-stressing software like Furmark was excluded from the test because one of the test materials, the GTX 580, is equipped with a power-monitoring feature that effectively cuts off overall power consumption.
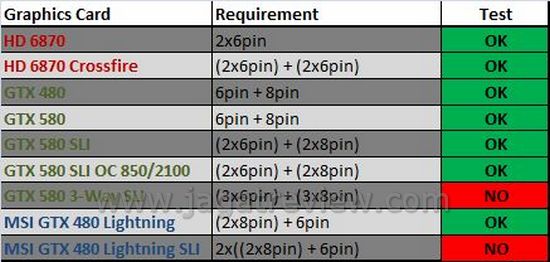
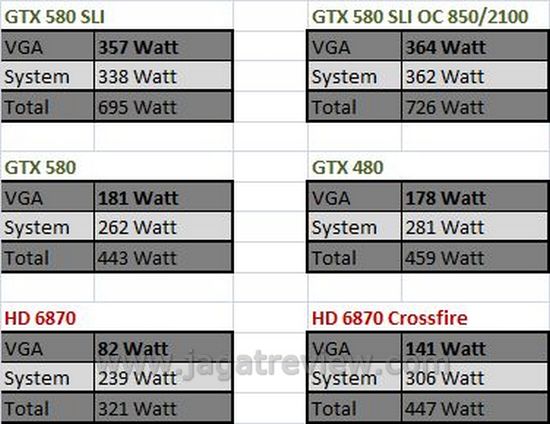
We ran into no problem whatsoever when running the test. No hang up/ freeze, nor crash. This is a good indication since it shows that the Thermaltake Power Express 650 provides enough power to allow the graphics cards to function normally. In fact, our overclocked GTX 580 SLI (the graphics cards themselves, not the entire system) configuration consumes “only” 364 watts of power, which is nowhere near the 650 watt maximum output offered by the Power Express 650. However, it must be noted that each PCI express supplies 75-100 watts of power to the graphics card installed on it. That lifted some weight off the Power Express 650. If only there were a third 8-pin and 6-pin connectors, perhaps we could squeeze some more out of the 650 watt capacity. The way we see it, there’s no way we can fully utilize the 650 watt available power since the output is limited to only two 6-pin and two 8-pin cables.